Previous
Having a Healthy Liver Boosts Immune Health
Next
A New Therapy Has Been Tested for its Capability of Fighting Liver Disease
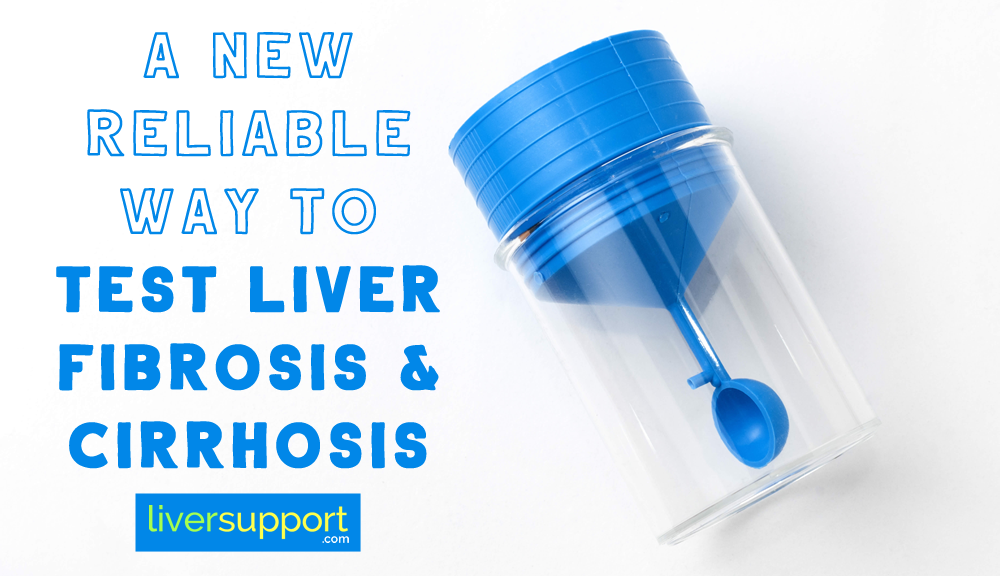
A New Reliable Way to Test Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Researchers from the University of San Diego and the Salt Lake Institute created a microbiome-based diagnostic tool which can detect fibrosis and liver cirrhosis with 90% reliability!
Liver disease is affecting approximately 844 million people worldwide and is one of the leading causes of death in many rich countries. When cirrhosis is in the early stages, many people don’t even show symptoms. The detection of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis is often found via routine blood tests or checkups.
Common Liver Disease Tests
Normally when there is a possibility of a problem with your liver, several tests will be done. According to Mayo Clinic (1) these include:
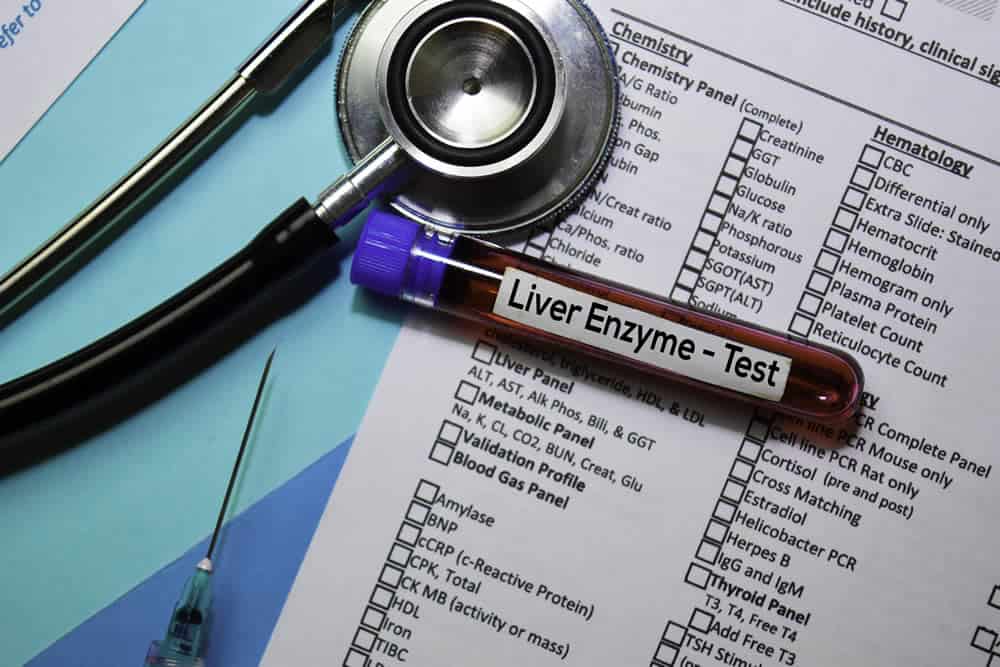
- Laboratory Tests – Blood tests can help show signs of liver malfunction by testing certain enzymes. These results may also help your doctor understand what the underlying cause is.
- Imaging Tests – These tests include MRI, CT, and ultrasounds which can detect hardening or stiffening of the liver.
- Biopsy – Taking a sample of the liver isn’t necessary for diagnosis but it can identify how severe liver damage is.
These tests come with concern though. Biopsies are invasive and painful, and not always reliable. MRIs and other imaging tests can be expensive and difficult to do in rural areas.
What Is This New Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Test?
Since difficulty of diagnosing liver disease is a concern, researchers from the University of San Diego and the Salt Lake Institute created a microbiome-based diagnostic tool. This tool can detect fibrosis and liver cirrhosis with 90% reliability in patients who are the greatest risk for cirrhosis.
The work of the researchers was published in the journal Cell Metabolism (2) on June 30, 2020. Professor Ronald Evans, a co-author of the published book, stated to Gilmore Health News (3) that “the microbiome is a living, dynamic sensor for small changes in the health and disease of the body and as such provides an accurate reading of the health of the body.”
This test is non-invasive, cost-effective, and based on an algorithm. All that is necessary is a stool sample, which can make it easy for locations that lack specialized clinics and physicians.

Liver disease has a specific “microbiome-derived signature” and the test developed is able to detect as many as 19 different bacterial strands in the stool that can cause liver disease. Researchers took samples from 163 healthy and sick volunteers. The microbiome-derived signature gave 94% accuracy with the diagnosis of cirrhosis and found the exact reason behind cirrhosis in over 90% of the patients.
Combining the signature, age, and serum albumin (a protein produced in the liver) levels in each participant allows scientists to distinguish cirrhosis in participants that differ between cause and geography.
This test is also capable of determining what stage liver fibrosis is at. This allows physicians to ensure a classification of disease for each patient and give them the best treatment strategy.
More Research Is Needed
Senior author Rohit Loomba, MD, professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and director of its NAFLD Research Center told Science News (4) in an interview that, “the next step is to establish causality of these gut microbial species or their metabolites in causing cirrhosis, and whether this test can be used and scaled up for clinical use.”
They are interested to see if removing certain bacteria will make the disease worse, or if restoring parts of the microbiome will return it to its healthy state.
With extensive knowledge on this it’s possible to be able to diagnose other severe diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other diseases that have been shown to be affected by microbiome.
Conclusion
With this new test, individuals who may be at risk for liver disease will have a non-invasive and affordable way to get a reliable diagnosis. No pokes, prods, or biopsies necessary.
Not only will this test give a clear diagnosis, but it’s possible the microbiome could be key to reversing liver disease and diagnosing other diseases where the cause can be uncertain. With over one quarter of the population dealing with chronic liver disease, this could be a breakthrough moment to reduce the odds of death from this progressive disease.
- (2018, December 07). Retrieved July 13, 2020, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cirrhosis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351492
- Oh, T. G., Kim, S. M., Caussy, C., Fu, T., Guo, J., Bassirian, S., . . . Loomba, R. (2020). A Universal Gut-Microbiome-Derived Signature Predicts Cirrhosis.Cell Metabolism. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.005
- Moore, M. (2020, July 07). Liver Disease: Stool Based Test Can Diagnose Cirrhosis With a 90% Accuracy. Retrieved July 14, 2020, from https://www.gilmorehealth.com/liver-disease-stool-based-test-can-diagnose-cirrhosis-with-a-90-accuracy/
- Universal gut microbiome-derived signature predicts cirrhosis. (2020, June 30). Retrieved July 13, 2020, from https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/06/200630125126.htm